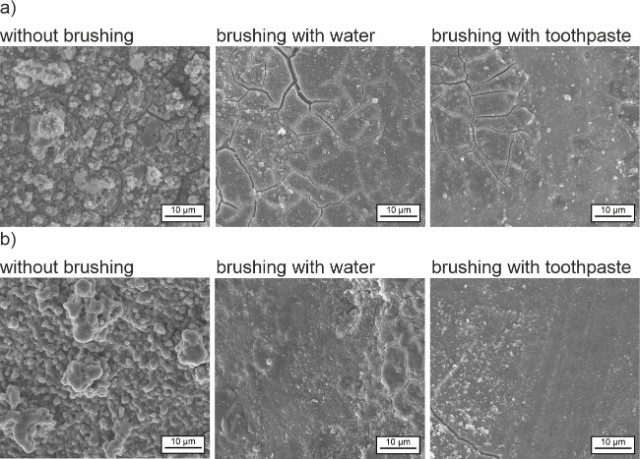
© Fraunhofer IMWS/Haleon
Antiseptic mouth rinses containing the active ingredient chlorhexidine (CHX) are widely used in dentistry. For many decades, CHX has set the gold standard for the management of oral diseases. During the treatment, however, tooth discoloration may occur after eating or drinking. A comprehensive in-vitro study conducted by the Fraunhofer Institute for Microstructure of Materials and Systems IMWS in Halle (Saale) has investigated the degree to which various beverages cause potential discoloration during chlorhexidine treatment. Based on the data collected, dental staff can now offer improved recommendations to patients about what they should do during the treatment period, for example: They should ideally always add milk when drinking tea or coffee.
MORE

